Search Resources
Pick a Topic
Topics
- Academic Support
- ADHD
- After Class
- AI
- Articles
- Attention
- Before Class
- Calendars
- Course Strategies
- Events
- Exam Prep
- Faculty & Advisors
- Finals
- Focus
- How To
- Learning & Memory
- Learning Essentials
- Memory
- Navigating Duke
- New Students
- Plan
- Planning
- Presentations
- Procrastination
- Reading
- Review
- Sleep
- Staff
- STEM
- Stress
- Study Spaces
- Technology & Apps
- Time Management
- Videos
Study Strategies That Work
To really learn the material it's not always about how much time you put in, it’s about how you use that time. Research shows that certain strategies can make learning stick longer and help you perform better on exams and assignments. The techniques below are all proven ways to move information into long-term memory and...Continue reading→
Self Explanation
What it is Self-explanation is the practice of pausing while you study to explain the material, either to yourself or someone else. You want to use your own words to talk through what the concept or idea means, how it works, or how you would teach it to someone else. Why it matters Explaining in...Continue reading→
Elaborative Interrogation
What Is Elaborative Interrogation? Elaborative interrogation a strategy that leverages questions and curiosity. Instead of just taking information at face value, you ask questions and seek answers to why it’s true or why it is happening, or how it connects to what you already know. Consider the difference between the statement “Important principles of chemistry”...Continue reading→
Metacognitive Cards
A tool to help you get things done.… Read MoreContinue reading→
Study for Exams with AI
There are a lot of pieces involved in studying for an exam. Here are a few ways that AI can help you navigate the process. What part of studying leads to the moment when something finally clicks for you? Do you feel confident creating your own practice questions or problems? What types of problems...Continue reading→
Synthesize & Review with AI
Reviewing your notes and materials in the 24 hours after class is a critical part of recalling and retaining the information in class. It is also where you start to synthesize and apply concepts. Review: Read notes and text material to fill in gaps Synthesize: Summarize your learning in a few sentences Question: Clarify...Continue reading→
Spaced Practice
What is Distributed or Spaced Practice? Distributed practice - or Spacing - is a technique commonly used when learning material or studying for a test. It involves creating a schedule of study sessions of short duration. These should be used to practice the same material - not new material. Distributed practice can be contrasted to...
Retrieval Practice
What is Retrieval Practice? Retrieval practice is the active process of trying to recall concepts and big ideas, even before we completely know our material. Instead of simply glancing over our notes, or passively underlining key words, retrieval practice engages a deep effort that strengthens recall to the point where it creates strong, long-term retention....Continue reading→
Interleaving
What is Interleaving? Interleaving is a learning technique where you purposefully mix up the topics you are reviewing and practicing within one study session. It is meant to replace blocked practice, where you only work on one topic for an extended period - such only practicing your multiplication tables while studying for math. Switching between...Continue reading→
Dual Coding
What is Dual Coding? Ever spend hours reading or studying, only to forget most of it the next day? Dual coding can help. This study strategy uses two forms of input — verbal (text or speech) and visual (images, diagrams, charts) — to help you understand and remember information more effectively. By engaging both the...
Learning STEM @Duke
The Academic Resource Center’s STEM Learning Consultants created a website to support both students and instructors of STEM courses, Learning STEM at Duke. Learning STEM at Duke introduces strategies, and the supporting research, to enhance learning in STEM courses at Duke. Learning STEM at Duke is intended for Duke undergraduate students and instructors who...Continue reading→
How to Read a Scientific Paper
How to read and understand a scientific paper: a guide for non-scientists London School of Economics and Political Science Jennifer Raff From vaccinations to climate change, getting science wrong has very real consequences. But journal articles, a primary way science is communicated in academia, are a different format to newspaper articles or blogs and require a level...Continue reading→
How long is short-term memory?
Shorter than you might think. Learning Scientists blog Yana Weinstein When I (or any cognitive psychologist) refer to “short-term memory”, we’re talking about memory that lasts for 15-30 seconds. Not minutes, not a day, not a few weeks. Just 15-30 seconds. This differs quite drastically from the way people commonly use the term “short-term memory”. Have...Continue reading→
The benefits of a good night’s sleep
TEDEd Shai Marcu Let’s Begin… It’s 4am, and the big test is in 8 hours. You’ve been studying for days, but you still don’t feel ready. Should you drink another cup of coffee and spend the next few hours cramming? Or should you go to sleep? Shai Marcu defends the latter option, showing how sleep...Continue reading→
Not All Stress is Bad (Video)
Extra Credit: Life’s Curiosities Explained (powered by Duke) Psychology professor, Dr. Bridgette Martin Hard talks about different types of stress, and how the night-before-the-exam stress can actually be helpful!
Memory & Review
We forget about 50% of new material within 24 hours. The figure below illustrates how quickly we forget the majority of new material encountered. So how can you remember? Below, you will find strategies for increasing memory retention, and being prepared for that exam without last minute cramming! Ways of Remembering The following are a few strategies that can help...Continue reading→
How Do I Use Past Exams?
There is a lot to learn from returned exams. Looking over past exams you can: Understand how the professor writes exam questions – if you are clear on what and how your professor asks questions will make it easier (and faster!) to interpret them on your next exam. Clarify what level of detail you are expected to know. Identify knowledge...Continue reading→
College Reading Tips
Download PDF: Reading Tips
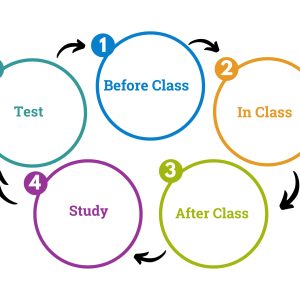
The Study Cycle
The study cycle is a guide to help you distribute your studying so you aren’t doing it all at once at the last minute, and to reinforce your learning from one step to the next. Download PDF: The Study Cycle
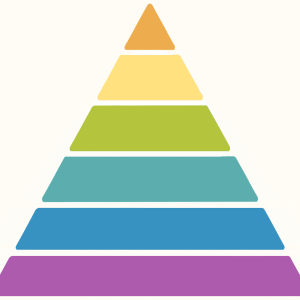
Blooms Taxonomy
Bloom's Taxonomy shows the six levels at which we can use knowledge.… Read MoreContinue reading→